Save to my favorites
What is it?
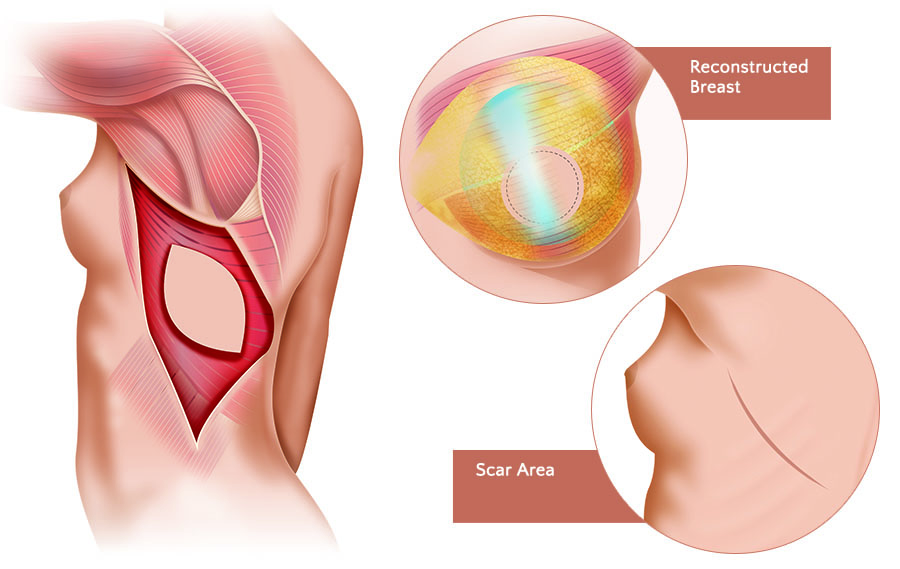
Lat dorsi reconstruction is a surgery that uses muscle and skin from your back to make a new breast. This approach usually also includes a tissue expander or breast implant.Read more:
The latissimus dorsi (or lat dorsi) is a back muscle located next to your shoulder blade. The lat dorsi flap may be used for additional coverage of a tissue expander and implant.
Because it has less fat than abdominal flaps used for breast reconstruction, the lat dorsi is the only tissue flap that usually requires an implant to provide enough volume (filler) for the new breast.
The lat dorsi is used in cases where the abdominal flaps are not available due to scarring from previous surgeries.
Tissue Expander
- An empty balloon made of silicone plastic with a small valve in its front wall
- The surgeon fills the expander with saline (salt water) through the valve
Implant
- Have round or teardrop shapes and covers made of silicone plastic
- Are filled with silicone gel or saline
- Silicone: a semi-solid gel
- Saline (Salt water)
How is it done?
A lat dorsi reconstruction usually involves a multiple step process over the course of about 3 to 5 months.
The surgeon moves skin, fat, and muscle from your back to the breast area, and places a tissue expander or implant under the flap. In cases where a tissue expander is used, the expander is filled over the course of one to two months, and later replaced with an implant.
In some cases, the surgeon may be able to place a saline or silicone gel implant at the same time as the flap operation, without needing to insert a tissue expander first.
Learn more about the steps
Start
Lat Dorsi Flap Surgery with Tissue Expander Placement
- Reconstruction can begin at the same time as your mastectomy, or can be done later
- The surgeon makes an incision in your upper or lower back
- The muscle and an attached piece of overlying skin are lifted off of the chest wall
- The muscle-skin flap is then tunneled through the armpit and into the mastectomy site
- The flap is then used to provide covering for a tissue expander or, in some cases, a saline or silicone gel implant
- The donor site on the back is closed in a straight line, leaving a flat contour
2 - 4 weeks
Tissue Expansion Process
- Multiple visits to your surgeon (about 4 to 8 visits)
- Visits are 1 to 2 weeks apart
- At each visit, the surgeon injects saline (salt water) into the tissue expander
- As the tissue expander gets bigger, it makes the skin grow, creating the shape of the new breast
- Office visits for expansion usually take about 20 to 30 minutes
1 - 3 months
Rest Period
- No more expansion visits
- Gives your skin time to relax and finish growing
1 - 3 months
Replacement of Expander for Implant
- Surgeon removes expander and puts in the implant
- Takes about 1 to 2 hours
- Surgery does not usually require a hospital stay (outpatient)
3 Months
Nipple Reconstruction or other optional procedures
By the numbers
- Number of surgeries2 (if a tissue expander is used)
- Patients who have this type of reconstruction usually need 2 surgeries, because a tissue expander is needed to grow the flap tissue before inserting a saline or silicone gel implant:
- First surgery: to harvest the back flap and place the tissue expander *
- Second surgery: to remove the expander and get the silicone or saline implant
* The first operation (tissue expander) can often be combined with the mastectomy (immediate reconstruction).
- Nights in the hospital1 or 2 nights after the first operation
The lat dorsi reconstruction usually requires a 1 2 night hospital stay. The surgery that exchanges the expander for the implant usually does not require an overnight stay in the hospital.
Each surgery takes about 2 to 4 hours to complete.
- Length of recovery4 weeks
Restrictions usually include no driving for 2-3 weeks, and no physical work, heavy lifting or gym for 3-4 weeks.
You may need to limit activities for about 4 weeks following surgery. Healing and expansions take 2-3 months. The average time between first and last surgery is 3-5 months.
Even after the initial recovery time has passed, you still may not feel like yourself. You may still feel tired and sore for a few months after your surgeries.
What are the pros?
- Reliable
The lat dorsi reconstruction provides healthy, reliable skin and muscle for tissue expansion and maybe a good option for women who can't have other kinds of flap surgeries.
The lat dorsi may be the most likely to work (reliable) type of tissue flap
- Not likely to have blood flow (circulation) problems
Lat dorsi reconstructions rarely have blood flow (circulation) problems.
What are the cons?
- You will need more than one surgery
If a tissue expander is used with the lat dorsi flap, you will need a second operation to replace the expander with a saline or silicone gel implant.
- You will not be able to use only your own tissue for reconstruction
Some women prefer to use only their own tissue for reconstruction, and avoid using an implant. The lat dorsi reconstruction usually requires an implant.
- Major operation | Leaves a scar on the back
The lat dorsi reconstruction is a major operation that leaves a scar on the back, in addition to the mastectomy scar. The back scar may be hard to hide in certain types of clothing.
- Tissue expander will feel tight and may be uncomfortable at times
The expansion process can cause soreness in some patients. Other patients simply have a feeling of tightness for several days following each expansion.
What are the risks?
- Infection
- Infection rates following surgery are 3 to 4% (3 - 4 people out of 100).
- Bleeding
- Chances of abnormal bleeding following surgery are about 2% (2 out of 100 patients).
- Transferred tissue failure
-
Some patients have circulation problems in the first few days after surgery, but this is less common with the lat dorsi surgery than other kinds of reconstruction.
Problems with blood flow can sometimes lead to transferred tissue failure, or flap loss. Total flap losses happen in
1
% of women (1 out of 100)
Partial flap losses (portions of skin or fat) happen in less than
5% of women (5 out of 100)
Possible major complications
- Re-operation | Re-hospitalization | Reconstruction failure
- In general, there is a 18% chance of having a major complication after lat dorsi reconstruction. That means 18 women out of 100 will need one of the following:
- Re-operation (needing to have another, unexpected surgery)
- Re-hospitalization (needing to be admitted back into the hospital after surgery)
- Reconstruction failure (the reconstruction doesn't work)
How do other women feel about it?
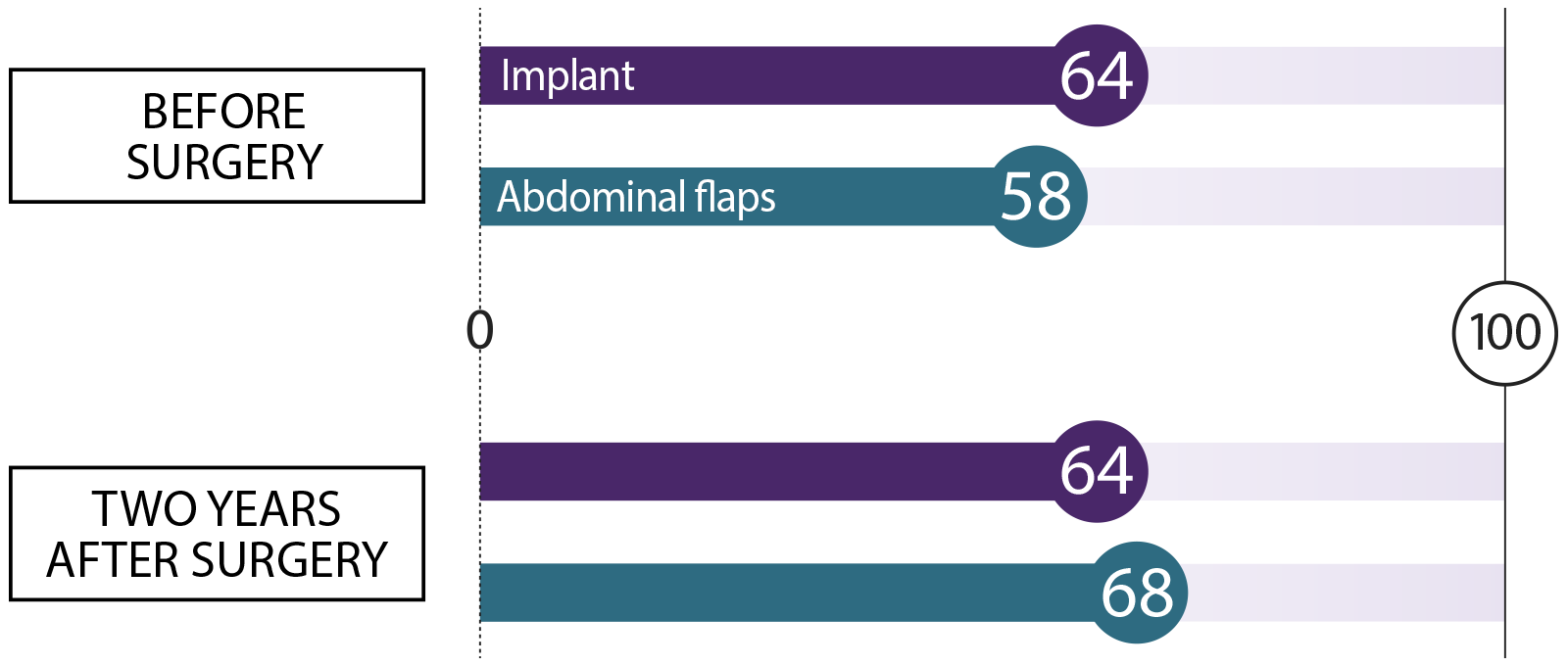
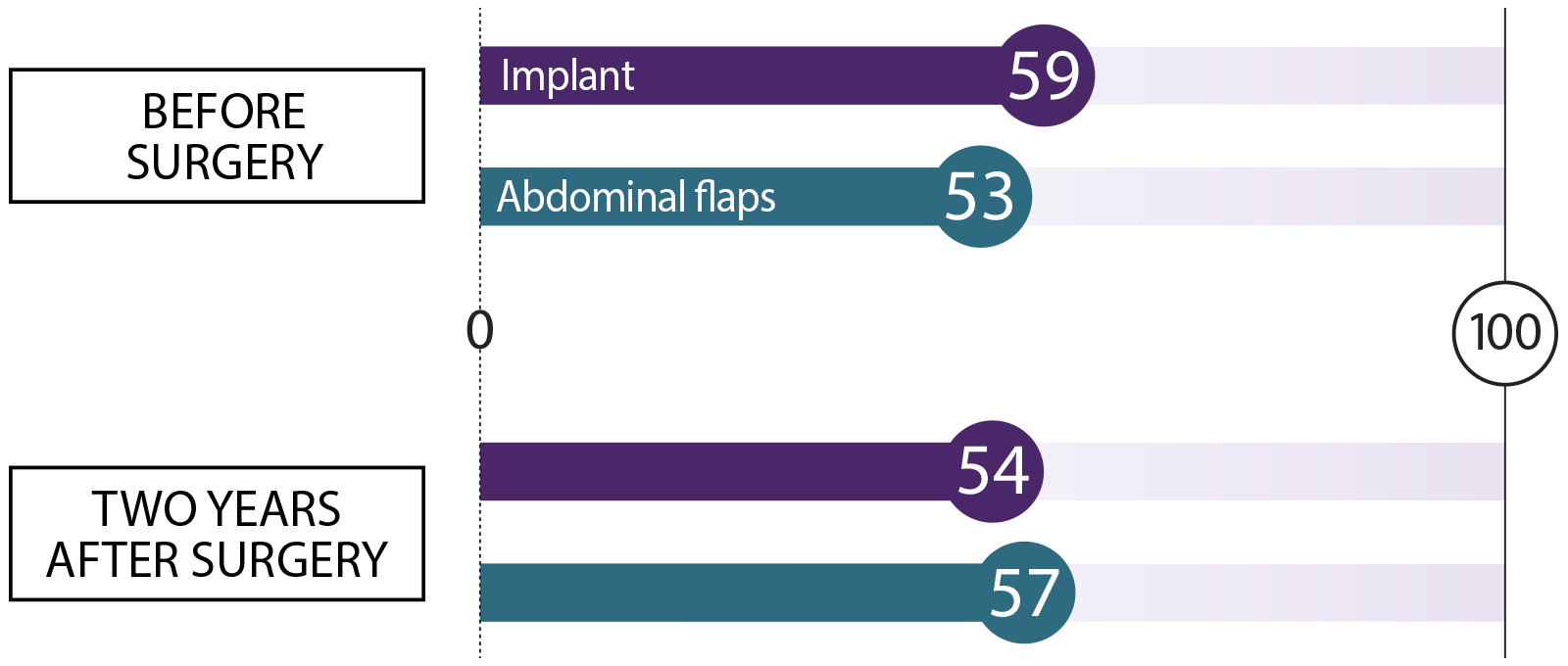
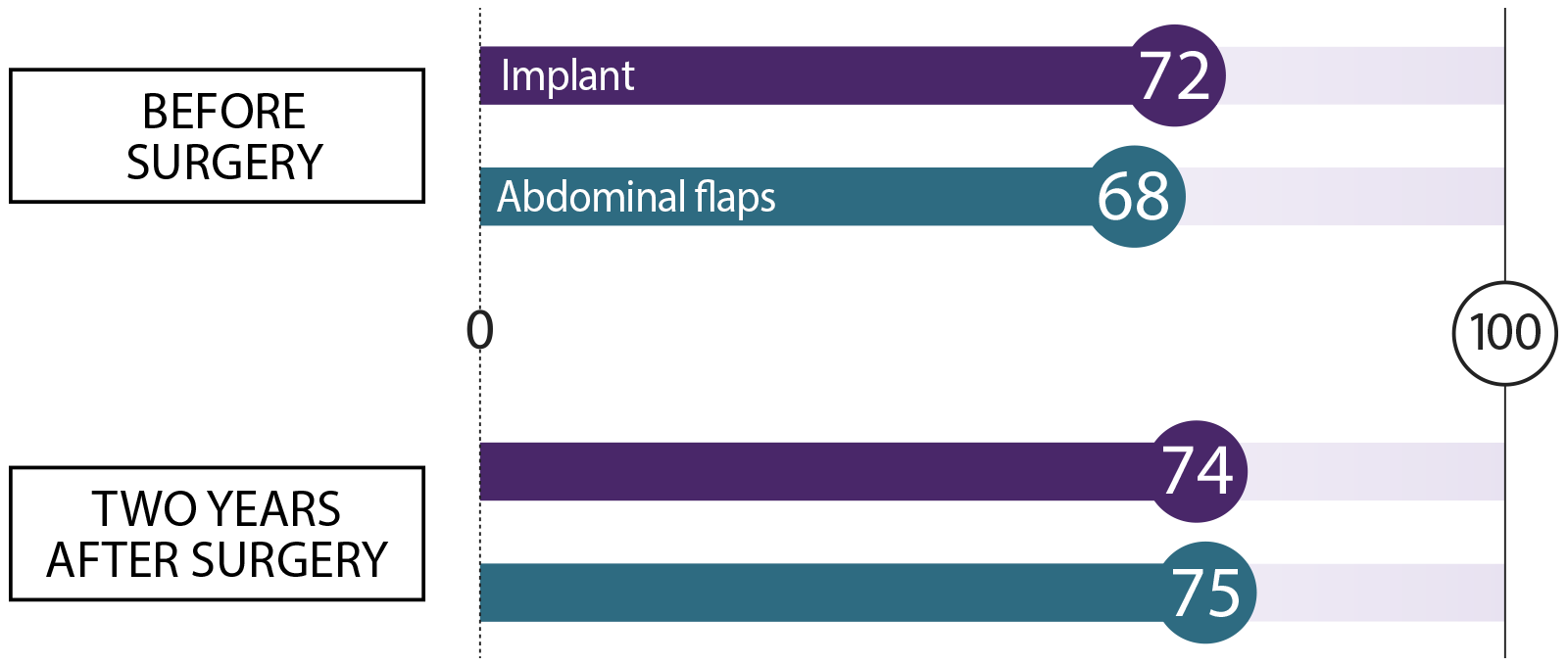
We asked women who had breast reconstruction how they felt before surgery and two years after their procedure. We asked about these topics. Here’s what they said:
Satisfaction with breasts How happy are you with the look and feel of your breasts?
 Sexual well-being
Sexual well-being How do you feel about your body as it relates to your sexuality?
 Psychosocial well-being
Psychosocial well-being How do you feel about your body image, and how confident are you in social settings?
 Physical well-being: Chest
Physical well-being: Chest How does your chest feel, physically?
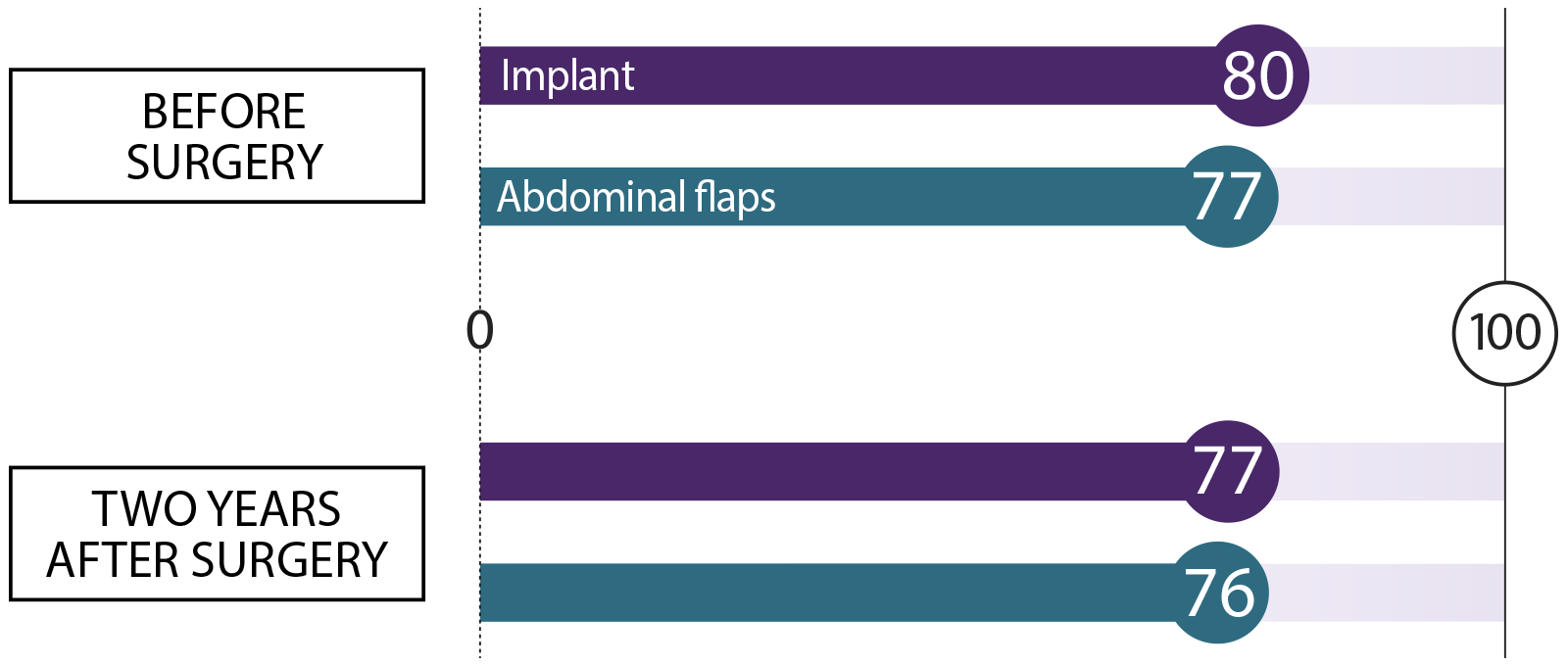 Physical well-being: Abdomen
Physical well-being: Abdomen How does your abdomen (stomach area) feel, physically?
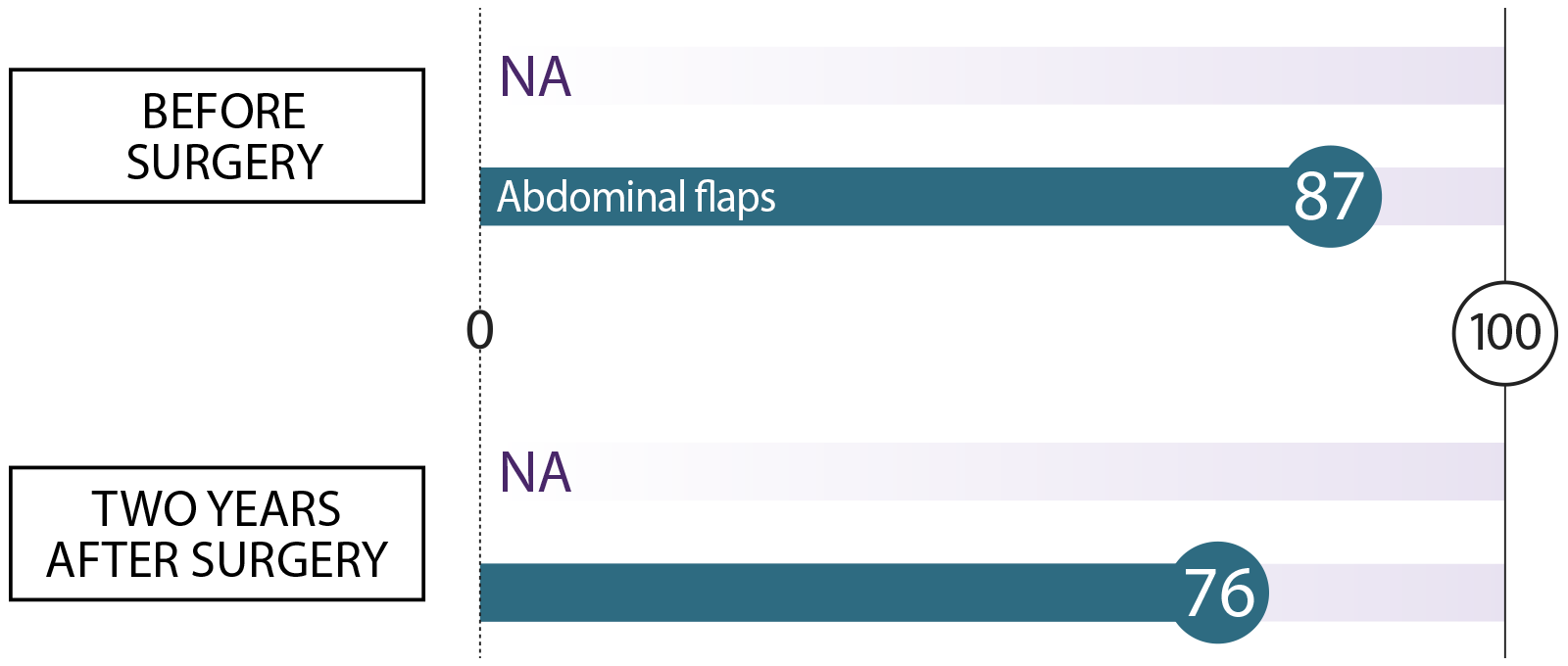

 Sexual well-being How do you feel about your body as it relates to your sexuality?
Sexual well-being How do you feel about your body as it relates to your sexuality?
 Psychosocial well-being How do you feel about your body image, and how confident are you in social settings?
Psychosocial well-being How do you feel about your body image, and how confident are you in social settings?
 Physical well-being: Chest How does your chest feel, physically?
Physical well-being: Chest How does your chest feel, physically?
 Physical well-being: Abdomen How does your abdomen (stomach area) feel, physically?
Physical well-being: Abdomen How does your abdomen (stomach area) feel, physically?